Delving into the realm of chemistry, we encounter a fundamental question that has puzzled scientists for centuries: Is FCL ionic or covalent? This intriguing inquiry invites us to explore the captivating world of chemical bonding, where the dance of electrons determines the very nature of matter.
Join us on this enthralling journey as we unravel the secrets of ionic and covalent compounds, delving into their properties, formation, and myriad applications.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will meticulously dissect the intricate tapestry of chemical bonds, providing lucid explanations and illustrative examples to illuminate this fascinating topic. Prepare to embark on an intellectual adventure that will forever alter your understanding of the molecular world.
Types of Chemical Bonds: Is Fcl Ionic Or Covalent
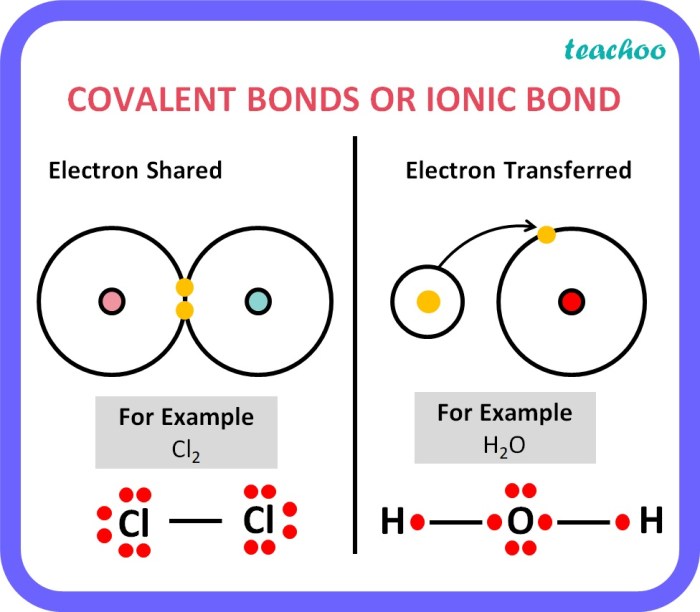
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together to form molecules and compounds. There are two main types of chemical bonds: ionic bonds and covalent bonds.
Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonds are formed between atoms of metals and non-metals. In an ionic bond, one atom gives up one or more electrons to another atom. The atom that gives up electrons becomes a positively charged ion, and the atom that receives electrons becomes a negatively charged ion.
Let’s switch gears for a moment and talk about food chains in the taiga. Read more to learn about the fascinating relationships between plants and animals in this unique ecosystem. Now, back to our original topic: is FCl ionic or covalent?
The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by the electrostatic force, forming an ionic bond.
Ionic bonds are typically strong and stable. They are found in many common compounds, such as sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium chloride (KCl).
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are formed between atoms of non-metals. In a covalent bond, the atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. The shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, forming a covalent bond.
Covalent bonds are typically weaker than ionic bonds. They are found in many organic compounds, such as methane (CH4) and ethane (C2H6).
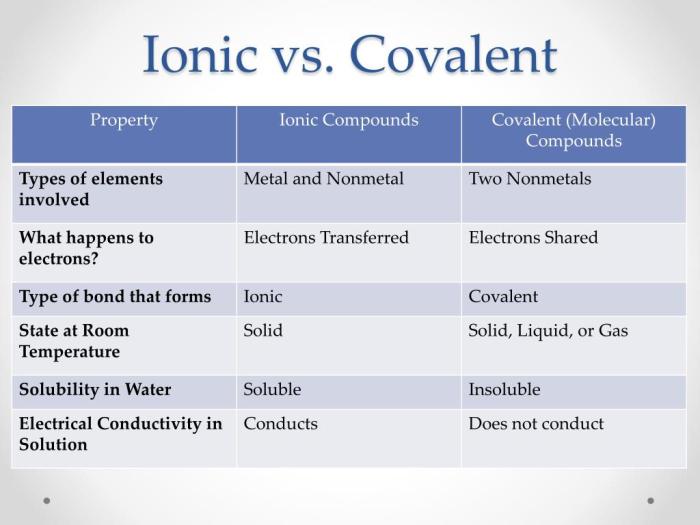
Properties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds
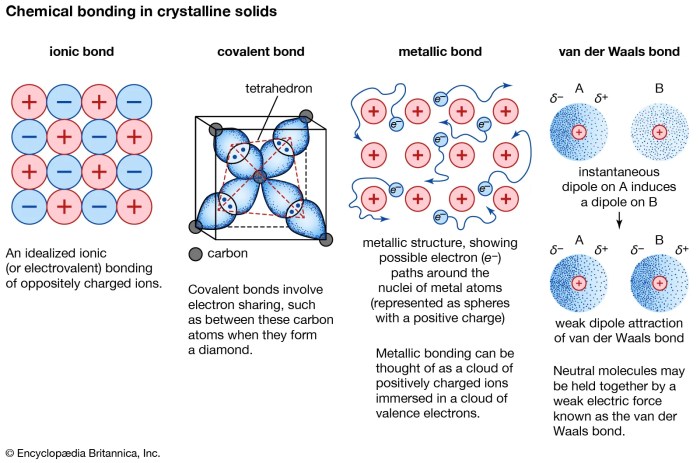
Ionic and covalent compounds exhibit distinct physical and chemical properties due to the nature of their chemical bonds. Let’s explore these properties and compare them.
Physical Properties
- Ionic Compounds:Typically solids at room temperature, with high melting and boiling points. They are brittle and have high electrical conductivity when dissolved in water or melted.
- Covalent Compounds:Can be solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature. They generally have lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds. They are soft and have poor electrical conductivity.
Chemical Properties
- Ionic Compounds:React readily with water to form ions, making them highly soluble in polar solvents. They undergo ionic reactions, where ions exchange to form new compounds.
- Covalent Compounds:Generally less reactive with water and do not ionize in solution. They undergo covalent reactions, where atoms share electrons to form new molecules.
Comparison of Properties, Is fcl ionic or covalent
| Property | Ionic Compounds | Covalent Compounds ||—|—|—|| Physical State | Solids | Solids, liquids, or gases || Melting/Boiling Points | High | Low || Brittleness | Brittle | Soft || Electrical Conductivity | High (in water/melted) | Poor || Solubility in Water | Soluble | Insoluble || Reactivity with Water | React readily | Less reactive || Type of Reactions | Ionic | Covalent |
Formation of Ionic and Covalent Bonds
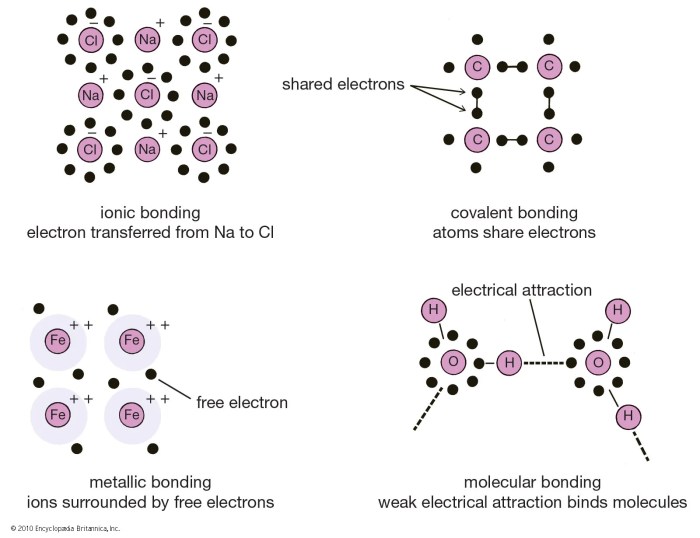
Ionic and covalent bonds are the two main types of chemical bonds. Ionic bonds are formed between atoms of metals and nonmetals, while covalent bonds are formed between atoms of nonmetals.
Ionic Bond Formation
Ionic bonds are formed when one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom. The atom that loses electrons becomes a positively charged ion, while the atom that gains electrons becomes a negatively charged ion. The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, forming an ionic bond.
Covalent Bond Formation
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. The shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, forming a covalent bond.
Comparison of Ionic and Covalent Bond Formation
Ionic and covalent bonds are formed by different mechanisms. Ionic bonds are formed by the transfer of electrons, while covalent bonds are formed by the sharing of electrons. Ionic bonds are typically formed between atoms of metals and nonmetals, while covalent bonds are typically formed between atoms of nonmetals.
Applications of Ionic and Covalent Compounds
Ionic and covalent compounds play crucial roles in various industries due to their unique properties. Let’s explore some of their practical applications:
Applications of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are widely used in:
- Table salt (sodium chloride):Preserving food and flavoring.
- Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate):As a leavening agent in baking and as an antacid.
- Fertilizers (ammonium nitrate):Providing nutrients for plant growth.
- Batteries (lithium-ion batteries):Storing and releasing electrical energy.
- Construction materials (cement):Binding materials in concrete and mortar.
Applications of Covalent Compounds
Covalent compounds find applications in:
- Plastics (polyethylene):Packaging, construction, and manufacturing.
- Fuels (methane):Natural gas used for heating, cooking, and power generation.
- Pharmaceuticals (aspirin):Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Solvents (acetone):Removing nail polish, cleaning, and degreasing.
- Adhesives (superglue):Bonding materials together.
Questions and Answers
What is the key difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
Ionic bonds arise from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, while covalent bonds result from the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
Can a single atom form both ionic and covalent bonds?
Yes, it is possible for an atom to participate in both ionic and covalent bonding, depending on the electronegativity of the atoms involved.
What factors influence the formation of ionic or covalent bonds?
The electronegativity difference between atoms, the size of the atoms, and the availability of electrons all play a role in determining the type of bond that forms.