What happens if goat siblings mate? This question delves into the complex realm of inbreeding, a practice that can have profound implications for the health, development, and genetic diversity of goat populations. By exploring the genetic, health, and ethical considerations surrounding goat sibling mating, this discussion aims to shed light on the potential risks and consequences of this practice.
Inbreeding, the mating of closely related individuals, can lead to an increased risk of genetic disorders and health problems. This is because siblings share a significant portion of their genetic material, which increases the likelihood of inheriting harmful recessive genes.
Moreover, inbreeding can compromise the immune system, making offspring more susceptible to disease.
Genetic Considerations
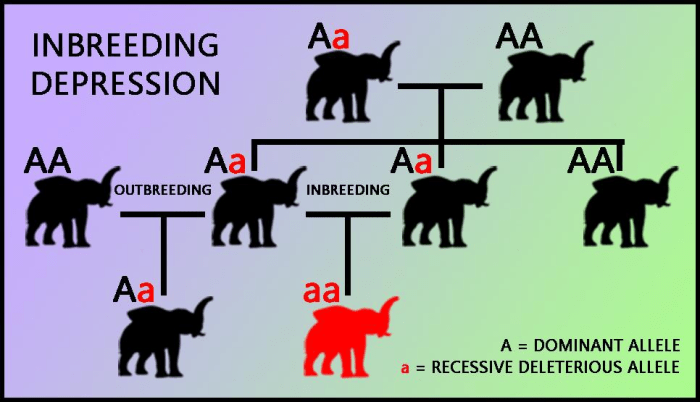
Inbreeding, the mating of closely related individuals, poses significant genetic risks in goats. It increases the likelihood of recessive genetic disorders, as siblings share a higher proportion of homozygous alleles than unrelated individuals. This can lead to the expression of harmful traits that would otherwise be masked by dominant alleles.
Examples of genetic disorders that can occur in goat siblings include congenital defects, metabolic disorders, and immune deficiencies.
Health and Development, What happens if goat siblings mate
Goat siblings mating can have detrimental effects on the health and development of their offspring. Inbred offspring are more susceptible to a range of health issues, including respiratory infections, digestive problems, and reproductive disorders. They may also exhibit developmental abnormalities, such as skeletal deformities and neurological impairments.
Additionally, inbreeding can weaken the immune system, making offspring more vulnerable to diseases and infections.
Fertility and Reproduction
Inbreeding can significantly impact fertility rates in goats. Inbred offspring often have reduced litter sizes and increased rates of infertility. This is due to the increased likelihood of genetic defects that can impair reproductive function. Inbred males may have lower sperm quality and reduced libido, while inbred females may experience difficulties with conception and pregnancy.
Breed Preservation and Genetic Diversity
Genetic diversity is crucial for the long-term survival and adaptability of goat populations. Inbreeding reduces genetic variation, making populations more vulnerable to disease outbreaks and environmental changes. It can also lead to the loss of valuable genetic traits, such as disease resistance, growth rate, and milk production.
In extreme cases, inbreeding can result in the extinction of entire breeds.
Ethical Considerations
The ethical implications of goat siblings mating are significant. Inbreeding can cause animal suffering due to the increased risk of genetic disorders and health problems. It can also raise concerns about the welfare of future generations, as inbred offspring may pass on harmful genetic traits to their own offspring.
Prevention and Management
Preventing goat siblings from mating is essential for maintaining healthy and genetically diverse goat populations. Responsible breeding practices, such as using unrelated breeding stock and maintaining accurate pedigrees, can help to minimize the risk of inbreeding. Additionally, separating siblings during the breeding season and implementing strict breeding protocols can further reduce the likelihood of inbreeding.
FAQs: What Happens If Goat Siblings Mate
What are the potential genetic risks of goat sibling mating?
Goat sibling mating increases the risk of recessive genetic disorders, as siblings share a significant portion of their genetic material. These disorders can include skeletal deformities, neurological problems, and immune deficiencies.
How does inbreeding affect the health of goat offspring?
Inbreeding can lead to developmental abnormalities, increased susceptibility to disease, and compromised immune function. Offspring from goat sibling mating may have reduced vigor, growth problems, and reproductive issues.
Can inbreeding reduce fertility rates in goats?
Yes, inbreeding can reduce fertility rates in goats. It can lead to smaller litter sizes, increased embryonic mortality, and reduced sperm quality. This can have a negative impact on the productivity and sustainability of goat breeding programs.