Embark on a scientific journey with the student exploration ionic bonds answer key, a comprehensive guide that unlocks the intricacies of ionic bonding. Delve into the fundamental principles, properties, and applications of ionic compounds, gaining a profound understanding of their significance in the chemical world.
Ionic bonding, a captivating concept in chemistry, involves the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of electrically charged ions. These ions, with their opposite charges, attract each other, forming stable ionic compounds. The strength of these bonds governs the physical and chemical properties of ionic compounds, influencing their solubility, melting point, reactivity, and conductivity.
Ionic Bond Definition and Formation: Student Exploration Ionic Bonds Answer Key

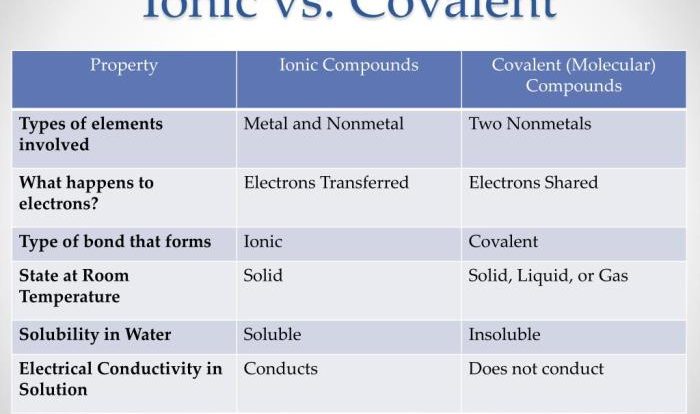
Ionic bonding is a chemical bond formed between two oppositely charged ions. It occurs when one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions.The transfer of electrons is driven by the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms.
Electronegativity is the measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons. The more electronegative an atom, the more strongly it attracts electrons.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are typically hard, brittle, and have high melting and boiling points. They are also good conductors of electricity when dissolved in water or melted.The physical properties of ionic compounds are due to the strong electrostatic forces between the positive and negative ions.
These forces hold the ions together in a rigid crystal lattice.The chemical properties of ionic compounds are also influenced by the electrostatic forces between the ions. Ionic compounds are generally unreactive because the ions are held together so tightly. However, they can react with other ionic compounds to form new compounds.
Applications of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are used in a wide variety of applications. Some common ionic compounds include sodium chloride (table salt), potassium chloride (fertilizer), and calcium carbonate (limestone).Ionic compounds are also used in a variety of industrial processes. For example, sodium hydroxide is used in the production of paper, soap, and detergents.
Hydrochloric acid is used in the production of plastics, dyes, and fertilizers.Ionic compounds are also important in biological systems. For example, sodium and potassium ions are essential for the proper functioning of nerve cells. Calcium ions are essential for the proper functioning of bones and teeth.
Comparison with Other Bond Types
Ionic bonding is one of the three main types of chemical bonds, along with covalent bonding and metallic bonding.Ionic bonds are typically stronger than covalent bonds, but weaker than metallic bonds. Ionic bonds are also more polar than covalent bonds, meaning that the electrons are not shared equally between the two atoms.The
type of bond that forms between two atoms depends on the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms. If the difference in electronegativity is large, an ionic bond will form. If the difference in electronegativity is small, a covalent bond will form.
Demonstration of Ionic Bond Formation
The formation of an ionic bond can be demonstrated by the following experiment:
- Place a piece of sodium metal in a clean glass jar.
- Add a few drops of water to the jar.
- Observe the reaction.
The sodium metal will react with the water to form sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. The sodium hydroxide is an ionic compound that is composed of sodium ions and hydroxide ions.The reaction can be represented by the following equation:
Na + 2 H2O → 2 NaOH + H2
Table of Common Ionic Compounds
| Ionic Compound | Chemical Formula | Charge | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium chloride | NaCl | +1,
|
Table salt, food preservative |
| Potassium chloride | KCl | +1,
|
Fertilizer, food additive |
| Calcium carbonate | CaCO3 | +2,
|
Limestone, cement |
| Sodium hydroxide | NaOH | +1,
|
Paper production, soap making |
| Hydrochloric acid | HCl | +1,
|
Plastic production, dye production |
Interactive Quiz on Ionic Bonding, Student exploration ionic bonds answer key
- *Multiple Choice
- Which of the following is NOT a property of ionic compounds?
(a) Hard (b) Brittle (c) Malleable (d) High melting point
Which of the following is a common ionic compound used as a fertilizer?
(a) Sodium chloride (b) Potassium chloride (c) Calcium carbonate (d) Hydrochloric acidTrue/False
- Ionic bonds are formed when two atoms share electrons.
- The strength of an ionic bond is directly proportional to the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms.
Short Answer
- Describe the process of electron transfer in ionic bond formation.
- Explain how the properties of ionic compounds are influenced by the electrostatic forces between the ions.
Query Resolution
What is the key characteristic of ionic bonding?
Ionic bonding is characterized by the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, formed when one atom transfers electrons to another.
How do ionic compounds differ from covalent compounds?
Ionic compounds result from the complete transfer of electrons, leading to the formation of ions, while covalent compounds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms.
What factors influence the strength of ionic bonds?
The strength of ionic bonds is primarily determined by the charges of the ions involved and the distance between them.