Embark on an enlightening journey into the atomic structure and periodic table worksheet, an invaluable resource that unravels the intricate world of elements and their properties. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental building blocks of matter, providing a profound understanding of the periodic table’s organization and its profound implications in various scientific disciplines.
Through engaging explanations, illustrative diagrams, and thought-provoking exercises, this worksheet empowers learners to grasp the concepts of atomic structure, including the nucleus, electrons, and electron shells. It explores the properties of protons, neutrons, and electrons, elucidating their contributions to an atom’s overall structure.
Atomic Structure
An atom is the basic unit of matter and consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, while electrons orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells.
Properties of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
- Protonshave a positive charge and are found in the nucleus.
- Neutronshave no charge and are also found in the nucleus.
- Electronshave a negative charge and orbit the nucleus in shells.
Diagram of an Atom, Atomic structure and periodic table worksheet
The following diagram illustrates the structure of an atom:

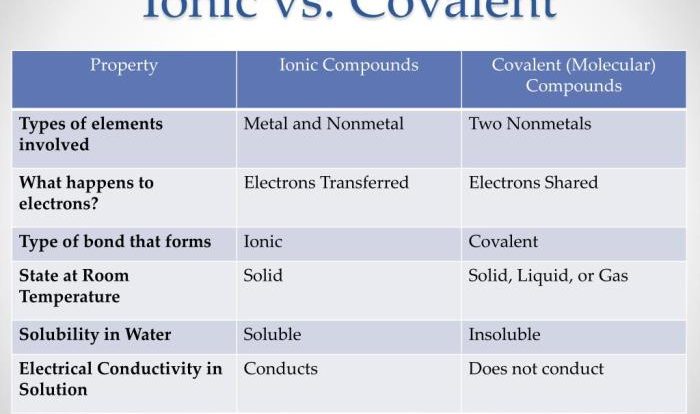
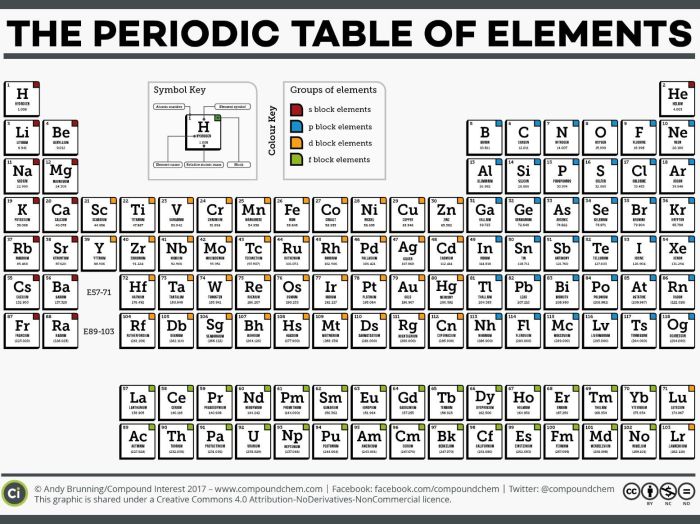
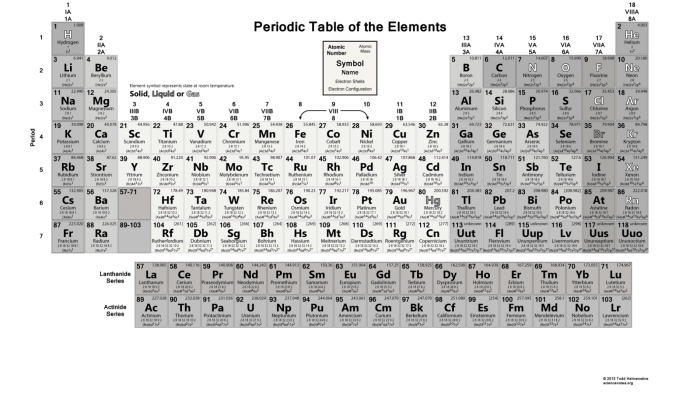
Periodic Table: Atomic Structure And Periodic Table Worksheet
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized based on their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. It consists of 18 vertical columns, called groups, and 7 horizontal rows, called periods.
Organization of the Periodic Table
- Groupsare numbered 1-18 from left to right and represent elements with similar chemical properties.
- Periodsare numbered 1-7 from top to bottom and represent elements with increasing atomic number.
Trends in the Periodic Table
- Atomic numberincreases from left to right across a period and from top to bottom down a group.
- Atomic massgenerally increases from left to right across a period and from top to bottom down a group.
- Chemical propertieschange systematically across the periodic table, with elements in the same group exhibiting similar reactivity.
Relationship between Atomic Structure and Periodic Properties
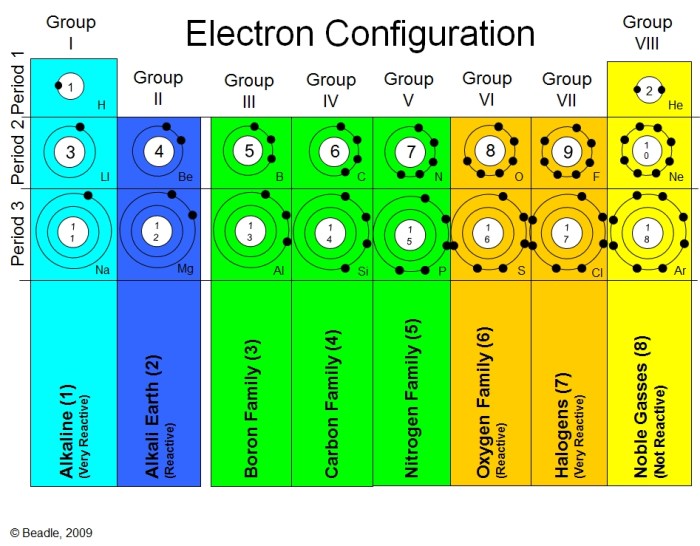
The atomic structure of an element determines its position in the periodic table and influences its chemical and physical properties.
Influence of Atomic Structure on Periodic Properties
- The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number and its position in the periodic table.
- The number of electrons in an atom determines its chemical reactivity.
- The number of neutrons in an atom affects its atomic mass and stability.
Predicting Properties from the Periodic Table
The periodic table can be used to predict the properties of an element based on its position in the table.
Applications of Atomic Structure and Periodic Table
Knowledge of atomic structure and the periodic table has wide-ranging applications in various fields of science and technology.
Applications in Science and Technology
- Material science: Designing new materials with specific properties.
- Drug development: Understanding the structure and properties of molecules to develop new drugs.
- Chemical reactions: Predicting the outcome of chemical reactions based on the properties of the elements involved.
Limitations and Evolution of the Periodic Table
While the periodic table is a powerful tool, it has certain limitations and continues to evolve as new discoveries are made.
Clarifying Questions
What is the significance of the periodic table?
The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic number, atomic mass, and chemical properties, providing a systematic framework for understanding and predicting the behavior of elements.
How does atomic structure influence an element’s position in the periodic table?
The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, which in turn dictates its position in the periodic table. Elements with similar atomic structures tend to exhibit similar chemical properties and are grouped together.
What are the limitations of the periodic table?
While the periodic table is a powerful tool, it has limitations. It does not account for the behavior of elements in compounds or the effects of temperature and pressure on their properties.