Embark on a journey into the realm of microbiology as we delve into the characteristics of bacteria worksheet answer key. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricate structure, diverse metabolism, and complex genetics of these remarkable microorganisms, providing a foundation for understanding their impact on our world.
From the fundamental components of a bacterial cell to the mechanisms of bacterial pathogenesis, this worksheet unravels the mysteries of bacterial biology. Prepare to immerse yourself in the fascinating world of bacteria and discover the answers to your most pressing questions.
Bacterial Cell Structure
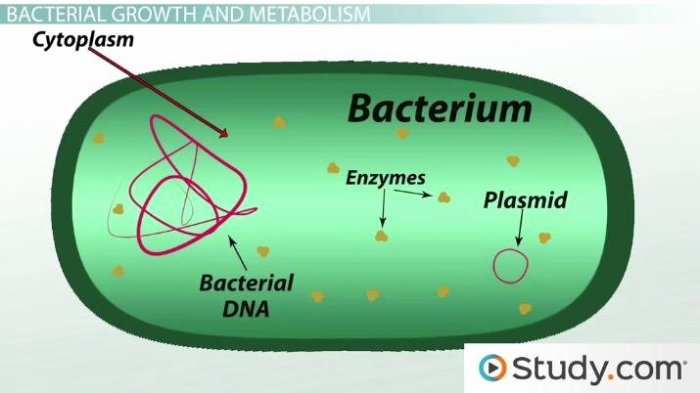
Bacterial cells are prokaryotic, meaning they lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. They have a simple cell structure that includes a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleoid.
The cell wall is a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and protects the cell from its surroundings. The cell membrane is a semi-permeable barrier that controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell. The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that fills the cell and contains all of the cell’s organelles.
The nucleoid is a region of the cytoplasm that contains the cell’s DNA.
Bacterial Growth and Reproduction
Bacteria reproduce asexually through binary fission, a process in which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Budding is another form of asexual reproduction in which a small bud forms on the side of the parent cell and eventually grows into a new cell.
Fragmentation is a third form of asexual reproduction in which a cell breaks into two or more pieces, each of which grows into a new cell.
The rate of bacterial growth is affected by a number of factors, including the availability of nutrients, the temperature, and the pH of the environment.
Bacterial Metabolism
Bacteria use a variety of metabolic pathways to generate energy and synthesize new cell material. Aerobic respiration is a metabolic pathway that requires oxygen and produces carbon dioxide and water as waste products. Anaerobic respiration is a metabolic pathway that does not require oxygen and produces a variety of waste products, including lactic acid, ethanol, and hydrogen sulfide.
Fermentation is a metabolic pathway that does not require oxygen and produces organic acids as waste products.
Some bacteria are obligate aerobes, meaning they can only grow in the presence of oxygen. Other bacteria are obligate anaerobes, meaning they can only grow in the absence of oxygen. Facultative anaerobes can grow in either the presence or absence of oxygen.
Bacterial Genetics
The bacterial chromosome is a single, circular DNA molecule that is located in the nucleoid. Bacteria also have plasmids, which are small, circular DNA molecules that are not essential for growth.
Bacteria can exchange genetic material through a process called transformation, in which DNA from one bacterium is taken up by another bacterium. Conjugation is a process in which DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another through a physical connection.
Transduction is a process in which DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a virus.
Bacterial Pathogenesis
Bacterial pathogenesis is the study of how bacteria cause disease. Bacteria can cause disease by producing toxins, damaging host cells, or by competing with the host for nutrients.
Some of the most common bacterial pathogens include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli. These bacteria can cause a variety of diseases, including pneumonia, sepsis, and urinary tract infections.
Bacterial Taxonomy and Classification
Bacterial taxonomy is the study of the classification of bacteria. Bacteria are classified into different groups based on their morphology, physiology, and genetic characteristics.
The most common system of bacterial classification is the Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, which divides bacteria into four main groups: the Gram-positive bacteria, the Gram-negative bacteria, the archaea, and the mycoplasmas.
Bacterial Ecology: Characteristics Of Bacteria Worksheet Answer Key
Bacteria are found in a wide variety of habitats, including soil, water, air, and the bodies of plants and animals. Bacteria play an important role in the cycling of nutrients and the decomposition of organic matter.
Bacteria can also form symbiotic relationships with other organisms. For example, some bacteria live in the digestive tracts of animals and help them to digest food. Other bacteria live on the skin of plants and help to protect them from pathogens.
Questions Often Asked
What is the significance of bacterial cell walls?
Bacterial cell walls provide structural support, protect against osmotic pressure, and facilitate interactions with the environment.
How do bacteria reproduce?
Bacteria primarily reproduce through binary fission, where one cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
What are the different types of bacterial metabolism?
Bacteria exhibit diverse metabolic capabilities, including aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration, and fermentation.
How do bacteria cause disease?
Bacteria can cause disease through various mechanisms, including the production of toxins, invasion of host tissues, and disruption of normal cellular functions.
What is the importance of bacterial taxonomy and classification?
Bacterial taxonomy and classification help identify and characterize different bacterial species, enabling effective diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of bacterial infections.