Embark on an enlightening journey through the byzantine empire worksheet answer key, a comprehensive guide to the enigmatic Byzantine Empire. This meticulously crafted resource unravels the complexities of this extraordinary civilization, providing a wealth of insights into its origins, achievements, and enduring legacy.
Delve into the fascinating history of the Byzantine Empire, tracing its rise from the ashes of the Roman Empire to its eventual decline. Explore the empire’s political and administrative structures, gaining a deep understanding of its governance and societal organization.
The Byzantine Empire: A Historical Overview
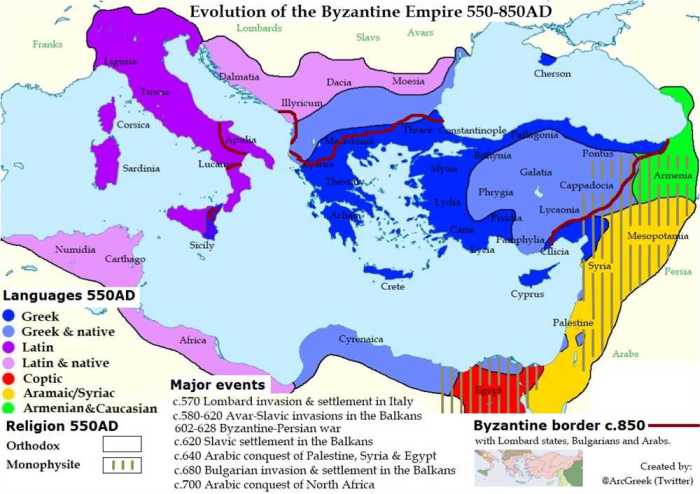
The Byzantine Empire emerged as the eastern half of the Roman Empire after the division in 395 CE. It lasted for over a millennium, playing a pivotal role in the development of Eastern Europe, the Mediterranean world, and beyond.
Origins and Establishment
The origins of the Byzantine Empire can be traced back to the reign of Emperor Constantine I (306-337 CE), who shifted the capital of the Roman Empire to Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul). After the division of the empire, the eastern half came to be known as the Byzantine Empire, named after its capital.
Major Events and Periods
- Justinian’s Reign (527-565 CE):Emperor Justinian I embarked on an ambitious project to reconquer lost territories and codify Roman law, resulting in the creation of the Justinian Code.
- The Iconoclast Controversy (726-843 CE):A period of religious turmoil that saw the destruction of religious images, known as icons.
- The Macedonian Renaissance (867-1056 CE):A cultural and economic revival marked by advancements in art, architecture, and literature.
- The Fourth Crusade (1204 CE):A turning point in Byzantine history, as Western European crusaders sacked Constantinople and established the Latin Empire.
Political and Administrative Structure
The Byzantine Empire was ruled by an emperor who held absolute power. The empire was divided into provinces, each governed by a governor. The Byzantine government was highly bureaucratic and centralized, with a complex system of laws and regulations.
The Byzantine Empire: Cultural Achievements
Art and Architecture
Byzantine art and architecture were renowned for their grandeur and opulence. The empire’s iconic churches, such as the Hagia Sophia, featured elaborate mosaics, frescoes, and domes.
Religious Art
Byzantine religious art played a crucial role in shaping the development of Christian iconography. The empire’s artists created stunning depictions of Christ, the Virgin Mary, and other saints, which became models for later Western art.
Preservation of Classical Knowledge, The byzantine empire worksheet answer key
The Byzantine Empire played a vital role in preserving and transmitting classical knowledge. Scholars in Constantinople collected and studied ancient Greek and Roman texts, ensuring their survival for future generations.
The Byzantine Empire: Military and Economic Power
Military Organization and Tactics
The Byzantine army was one of the most formidable in the world. It relied on a combination of heavy infantry, cavalry, and archers, supported by a sophisticated system of fortifications and siege warfare.
Economic Prosperity and Trade Networks
The Byzantine Empire enjoyed considerable economic prosperity, thanks to its control over major trade routes and its thriving manufacturing sector. The empire’s merchants traded with regions as far away as China and India.
International Diplomacy and Conflict
The Byzantine Empire played a key role in international diplomacy and conflict. It maintained diplomatic relations with various kingdoms and empires, and fought numerous wars against the Persians, Arabs, and later the Ottoman Turks.
The Byzantine Empire: Religion and Society
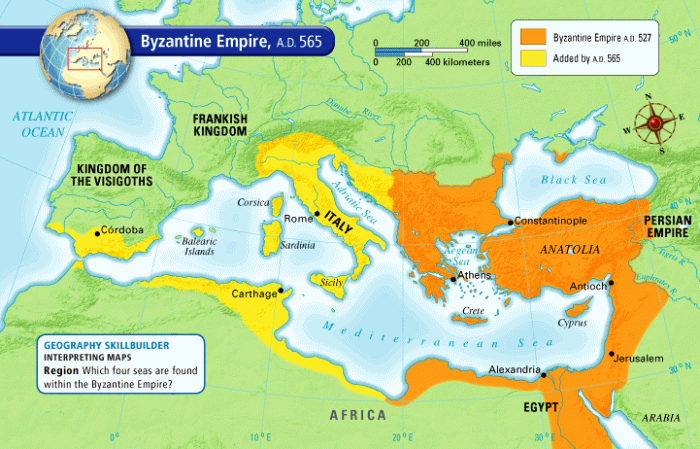
Role of Christianity
Christianity was the official religion of the Byzantine Empire. The emperor held a special role as protector of the faith, and the patriarch of Constantinople was the head of the Eastern Orthodox Church.
Relationship between Emperor and Patriarch
The relationship between the emperor and the patriarch was complex and often strained. The emperor claimed authority over religious matters, while the patriarch asserted the independence of the church.
Social Structure and Daily Life
Byzantine society was hierarchical, with the emperor at the top. The upper classes included the aristocracy, clergy, and wealthy merchants. The lower classes consisted of peasants, artisans, and slaves.
The Byzantine Empire: Legacy and Impact: The Byzantine Empire Worksheet Answer Key
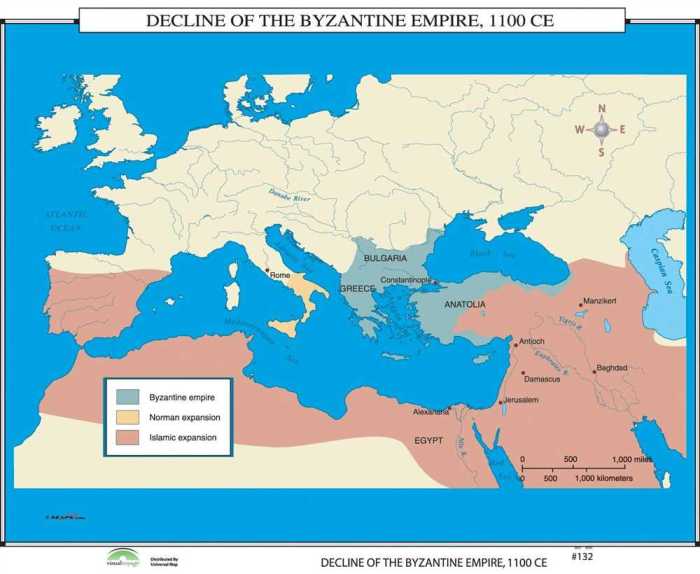
Decline and Fall
The Byzantine Empire began to decline in the 11th century, facing pressure from the Seljuk Turks and internal divisions. The empire’s final blow came in 1453 CE, when the Ottoman Turks conquered Constantinople.
Lasting Legacy
Despite its fall, the Byzantine Empire left a lasting legacy on Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean world. Its art, architecture, and religious traditions influenced cultures from Russia to Greece.
Influence on Modern Scholarship and Culture
The Byzantine Empire continues to fascinate scholars and inspire artists today. Its history, culture, and achievements provide valuable insights into the development of Western civilization.
Top FAQs
When was the Byzantine Empire founded?
The Byzantine Empire was founded in 330 AD by Emperor Constantine I.
What was the capital of the Byzantine Empire?
The capital of the Byzantine Empire was Constantinople, formerly known as Byzantium.
Who was the most famous Byzantine emperor?
Justinian I, who reigned from 527 to 565 AD, is considered the most famous Byzantine emperor.
