Like hard skills soft skills are learnable – Like hard skills, soft skills are learnable, and both are essential for career success. This article explores the similarities and differences in learning hard and soft skills, providing strategies for effectively acquiring and developing both types of skills for a well-rounded professional profile.
Hard skills, such as technical proficiency or specialized knowledge, are often acquired through formal education or on-the-job training. Soft skills, on the other hand, encompass interpersonal abilities, communication skills, and emotional intelligence, which can be developed through practice, self-reflection, and feedback.
Learnability of Hard Skills
Hard skills refer to specific, technical abilities that are acquired through education, training, or experience. These skills are essential for performing job tasks and achieving organizational goals. Examples of hard skills include programming, accounting, engineering, and data analysis.
Hard skills are learnable through a combination of formal education, on-the-job training, and self-study. Educational programs such as degree or certification courses provide a structured approach to learning the fundamentals of a particular skill. On-the-job training involves working under the guidance of an experienced professional, while self-study can be done through online courses, books, or other resources.
Effective learning strategies for hard skills include:
- Breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps
- Regular practice and repetition
- Seeking feedback from experts or mentors
- Applying skills in real-world situations
Learnability of Soft Skills
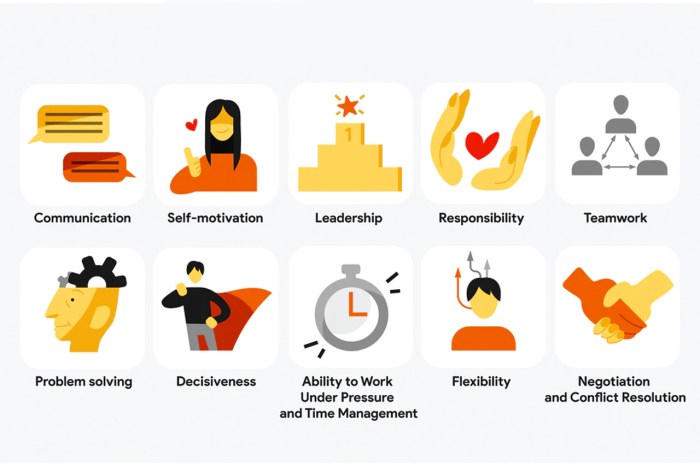
Soft skills encompass interpersonal, communication, and emotional intelligence abilities that are crucial for workplace success. These skills include teamwork, communication, problem-solving, critical thinking, and emotional regulation.
Soft skills are acquired through a combination of experience, observation, and training. While some soft skills may be innate, they can be developed and enhanced through workshops, seminars, and coaching. Role-playing, simulations, and case studies are common methods used in soft skills training.
Methods for acquiring and enhancing soft skills include:
- Observing and emulating successful individuals
- Actively seeking feedback from colleagues and superiors
- Participating in team projects and collaborative initiatives
- Reading books and articles on soft skills development
Similarities in Learning Hard and Soft Skills
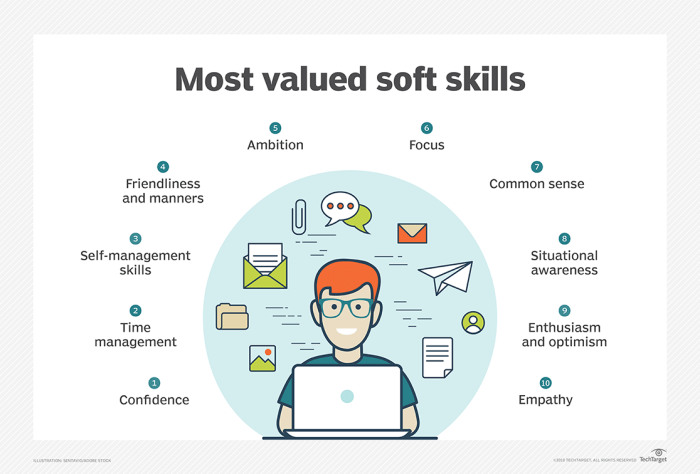
Despite their differences, there are commonalities in the learning processes for both hard and soft skills. Both types of skills require:
- Practice and repetition
- Feedback and guidance
- Application in real-world situations
The table below compares the approaches to learning hard and soft skills:
| Hard Skills | Soft Skills | |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition | Formal education, training, self-study | Experience, observation, training |
| Learning Methods | Structured courses, on-the-job training | Workshops, seminars, coaching |
| Feedback | Objective, measurable | Subjective, qualitative |
| Application | Technical tasks | Interpersonal interactions |
Differences in Learning Hard and Soft Skills
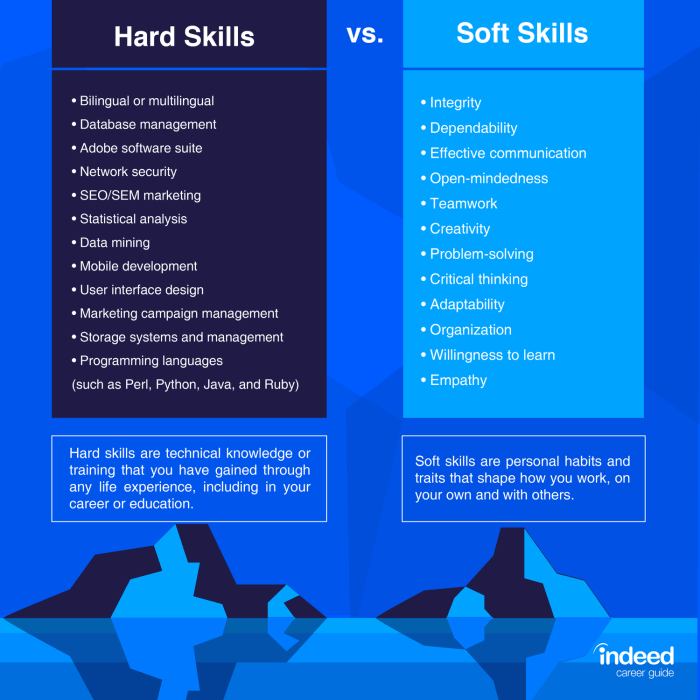
While there are similarities in learning hard and soft skills, there are also unique challenges and opportunities in each type of skill development. Hard skills are often more structured and quantifiable, while soft skills can be more subjective and difficult to measure.
The following are some key differences in their learning methodologies:
- Hard skills often have clear learning paths and established standards, while soft skills may require more individualized approaches.
- Hard skills can often be acquired in a shorter timeframe compared to soft skills, which may take longer to develop and master.
- Hard skills are often more easily transferable across different industries, while soft skills may be more context-specific.
Importance of Continuous Learning: Like Hard Skills Soft Skills Are Learnable

In today’s rapidly changing workplace, continuous learning is essential for both hard and soft skills development. Embracing a growth mindset and seeking opportunities to enhance skills is crucial for career advancement and personal fulfillment.
Continuous learning can lead to:
- Increased job satisfaction and engagement
- Improved performance and productivity
- Greater adaptability to changing job demands
- Enhanced career opportunities
FAQ Overview
What are the key differences between hard and soft skills?
Hard skills are typically technical or specialized knowledge acquired through formal education or training, while soft skills are interpersonal abilities, communication skills, and emotional intelligence developed through practice and self-reflection.
Can soft skills be learned?
Yes, soft skills can be learned and improved through practice, self-reflection, feedback, and training programs.
Why is continuous learning important for career success?
Continuous learning allows individuals to adapt to the evolving job market, enhance their skills, and stay competitive in their field.