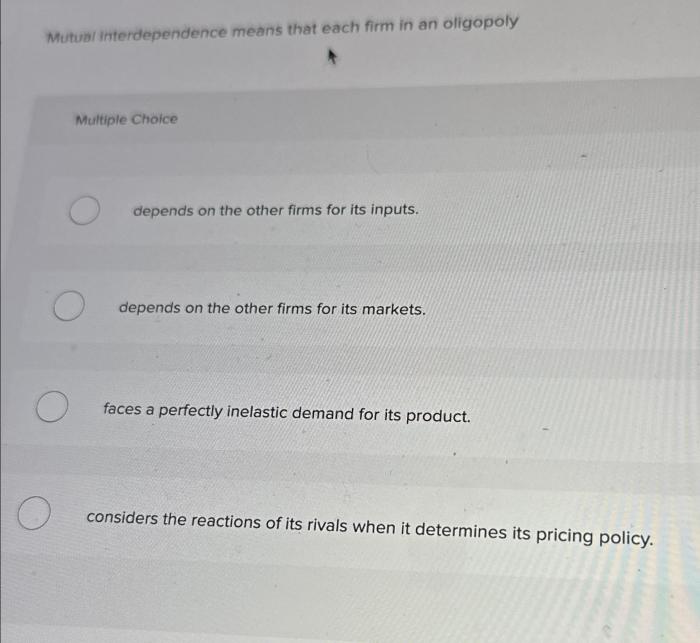
Mutual interdependence means that each oligopolistic firm recognizes the impact of its actions on its rivals and vice versa. This recognition shapes the pricing and output decisions of firms in oligopolistic markets, leading to complex interactions and strategic behavior.
Oligopolistic firms must consider the potential reactions of their competitors when setting prices and determining output levels. Interdependence creates a dynamic environment where firms must anticipate and respond to the moves of others, resulting in a delicate balance of competition and cooperation.
Market Structure and Oligopoly
Oligopoly is a market structure characterized by the presence of a small number of large firms that dominate the industry. Key characteristics of oligopoly include:
- High barriers to entry
- Interdependence among firms
- Non-price competition
Factors contributing to oligopoly formation include economies of scale, product differentiation, and government regulation.
Examples of oligopolistic industries include the automobile industry, telecommunications, and pharmaceuticals.
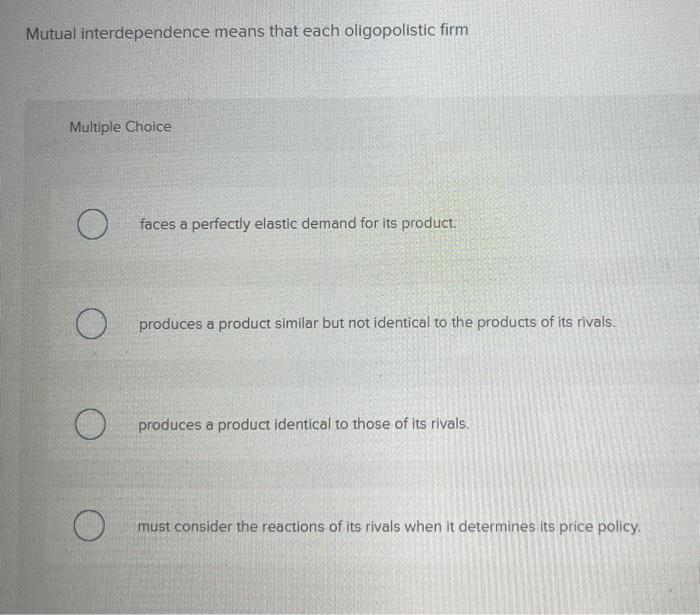
Interdependence in Oligopoly, Mutual interdependence means that each oligopolistic firm
Mutual interdependence in oligopoly refers to the situation where each firm’s decisions regarding price, output, and other strategic variables significantly affect the outcomes of other firms in the industry.
Interdependence arises from the limited number of firms and the high stakes involved in their interactions. Each firm must consider the potential responses of its rivals when making decisions.
Real-world examples of interdependence in oligopoly include the pricing wars between airlines and the competition for market share in the smartphone industry.
Collusion and Cooperation
Collusion occurs when oligopolistic firms agree to coordinate their actions to increase their collective profits. Potential benefits of collusion include higher prices, reduced competition, and increased market power.
However, collusion is challenging to maintain due to the risk of cheating and the difficulty of enforcing agreements. Successful examples of collusion include the OPEC cartel and the De Beers diamond cartel.
Failed attempts at collusion include the Microsoft-IBM alliance and the proposed merger between AT&T and T-Mobile.
Game Theory and Oligopoly
Game theory provides a framework for analyzing oligopolistic interactions. Nash equilibrium is a solution concept that predicts the outcome of a game where each player’s strategy is a best response to the strategies of all other players.
Game-theoretic models have been used to study various aspects of oligopolistic behavior, including pricing, output, and innovation.
Government Intervention and Regulation
Governments intervene in oligopolistic markets through antitrust laws and other regulatory measures to promote competition and protect consumer welfare.
Antitrust laws aim to prevent anti-competitive practices such as collusion and predatory pricing. Examples of government actions include the breakup of Standard Oil in 1911 and the antitrust case against Microsoft in the late 1990s.
Implications for Consumers and Society
Oligopoly can have both positive and negative implications for consumers and society.
- Positive:Oligopolistic firms may benefit from economies of scale, leading to lower costs and higher efficiency.
- Negative:Oligopoly can result in higher prices, reduced consumer choice, and slower innovation due to the lack of competition.
Policies to mitigate the negative effects of oligopoly include antitrust enforcement, price regulation, and promoting competition through new entrants.
FAQ Resource: Mutual Interdependence Means That Each Oligopolistic Firm
What is mutual interdependence in oligopoly?
Mutual interdependence in oligopoly refers to the situation where each firm recognizes that its actions, such as pricing and output decisions, will affect the behavior and profitability of its rivals.
How does interdependence affect pricing decisions in oligopoly?
Interdependence leads firms to consider the potential reactions of their competitors when setting prices. They may engage in price wars or collude to maintain higher prices, depending on the market conditions and the level of competition.
What is the Nash equilibrium in oligopoly?
The Nash equilibrium is a situation in which each firm chooses its best strategy given the strategies of its competitors. In oligopoly, the Nash equilibrium may involve firms setting prices and output levels that maximize their profits while considering the interdependence between them.