Embark on an enthralling journey into the realm of genetics with the Building DNA Gizmo Answer Key. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricacies of DNA, providing a step-by-step approach to understanding its structure, function, and significance in the world of biology.
Delving into the fundamentals, we’ll explore the building blocks of DNA, unravel the processes involved in its replication, and uncover the fascinating role of mutations in genetic variation. Prepare to be captivated as we unravel the secrets of DNA, one nucleotide at a time.
Building DNA Gizmo Overview
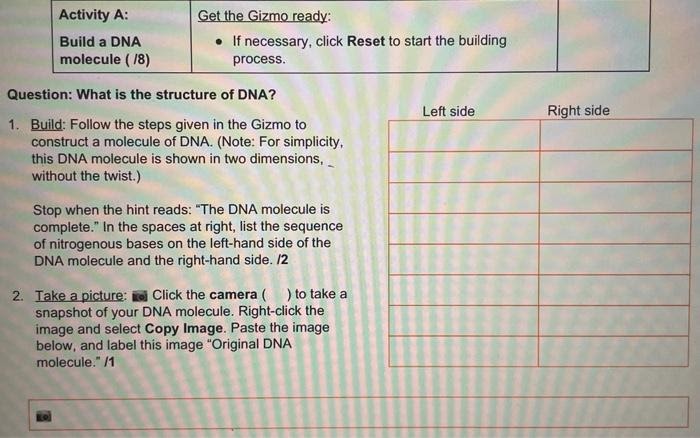
The Building DNA Gizmo is an interactive simulation that allows students to explore the structure and function of DNA. The Gizmo features a variety of tools that students can use to build and manipulate DNA molecules, including a base pair builder, a restriction enzyme cutter, and a DNA ligase.
The Gizmo is a valuable tool for teaching students about the basics of DNA structure and function. It can be used to demonstrate how DNA is synthesized, how it is replicated, and how it is used to code for proteins.
Key Components and Features
The Building DNA Gizmo has a number of key components and features, including:
- A base pair builder that allows students to build DNA molecules by adding and removing nucleotides.
- A restriction enzyme cutter that allows students to cut DNA molecules at specific locations.
- A DNA ligase that allows students to join DNA molecules together.
- A variety of visualization tools that allow students to view DNA molecules in different ways.
Step-by-Step Guide
To use the Building DNA Gizmo, students should follow these steps:
- Open the Gizmo and select the “Build a DNA Molecule” tab.
- Use the base pair builder to add nucleotides to the DNA molecule.
- Use the restriction enzyme cutter to cut the DNA molecule at specific locations.
- Use the DNA ligase to join the DNA molecules together.
- Use the visualization tools to view the DNA molecule in different ways.
DNA Structure and Function
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the genetic material that carries instructions for the development and functioning of all known living organisms. It is a molecule composed of a double helix structure, consisting of two strands twisted around each other.
Nucleotides
DNA is made up of repeating units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of three components: a nitrogenous base, a deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate group. There are four different types of nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).
I’m stuck on this Building DNA Gizmo assignment. It’s driving me nuts! I need to find the answer key, but it’s nowhere to be found. Maybe I should check out the Boyle’s and Charles Law Gizmo? Here it is . Oh, wait, this is not what I need.
Back to the Building DNA Gizmo…ugh!
Base Pairs
The nucleotides in DNA are arranged in a specific sequence. Adenine always pairs with thymine, and guanine always pairs with cytosine. These base pairs form the “rungs” of the DNA ladder, and the sequence of base pairs determines the genetic information carried by the DNA.
Double Helix
The two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. The double helix structure of DNA allows for easy replication, as the two strands can be separated and used as templates to create new strands.
Role of DNA
DNA plays a crucial role in storing and transmitting genetic information. It contains the instructions for the synthesis of proteins, which are the building blocks of cells. DNA is also responsible for cell division, ensuring that each new cell receives a complete copy of the genetic material.
Types of DNA, Building dna gizmo answer key
There are two main types of DNA: coding DNA and non-coding DNA. Coding DNA contains the instructions for making proteins, while non-coding DNA does not. Non-coding DNA plays a variety of roles, such as regulating gene expression and providing structural support for chromosomes.
Building a DNA Molecule

Building a DNA molecule with the Gizmo involves selecting nucleotides and connecting them to form base pairs. The Gizmo provides a virtual workspace where you can drag and drop nucleotides to create a DNA strand.
Selecting Nucleotides
The Gizmo offers a library of nucleotides, each representing one of the four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). To select a nucleotide, simply click on it in the library.
Connecting Nucleotides
Once you have selected two nucleotides, you can connect them to form a base pair. To do this, drag one nucleotide onto the other. The Gizmo will automatically align the nucleotides and form a hydrogen bond between them.
Types of Bonds
The DNA molecule is held together by two types of bonds: hydrogen bonds and covalent bonds. Hydrogen bonds form between the nitrogenous bases of complementary nucleotides (A-T and C-G). Covalent bonds form between the deoxyribose sugars and phosphate groups of adjacent nucleotides.
DNA Replication
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. This process is essential for cell division and growth.DNA replication occurs in three main steps:
- Initiation: The replication process begins when an enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA double helix, creating a replication bubble.
- Elongation: DNA polymerase, another enzyme, adds nucleotides to the growing DNA strands, using the original strands as templates.
- Termination: Once the entire DNA molecule has been replicated, the replication bubble closes and the DNA strands are sealed together by an enzyme called ligase.
Enzymes in DNA Replication
Several enzymes play essential roles in DNA replication, including:
- Helicase: Unwinds the DNA double helix.
- DNA polymerase: Adds nucleotides to the growing DNA strands.
- Ligase: Seals the DNA strands together.
Importance of DNA Replication
DNA replication is essential for cell division and growth because it ensures that each new cell receives a complete and accurate copy of the DNA. This process is also essential for DNA repair, as it allows cells to replace damaged or mutated DNA with new, undamaged DNA.
Mutations and Genetic Variation
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can occur due to various factors, such as exposure to environmental toxins, errors during DNA replication, or spontaneous chemical reactions. These changes can range from small alterations in a single nucleotide to large-scale rearrangements involving multiple genes.
Types of Mutations
* Point mutationsinvolve changes in a single nucleotide, such as a substitution, insertion, or deletion. These mutations can alter the amino acid sequence of a protein, potentially affecting its function.
- Frameshift mutationsresult from the insertion or deletion of nucleotides that alter the reading frame of the DNA sequence. This can lead to significant changes in the protein structure and function.
- Large-scale mutationsinclude inversions, translocations, and deletions, which involve the rearrangement or loss of large DNA segments. These mutations can disrupt gene regulation or cause the loss of essential genes.
Role in Genetic Variation and Evolution
Mutations are a primary source of genetic variation within populations. By introducing changes in the DNA sequence, mutations can create new alleles that can be inherited by offspring. This variation provides the raw material for natural selection, which favors alleles that enhance an organism’s survival and reproduction.
Over time, the accumulation of beneficial mutations can lead to the evolution of new species.
Applications of DNA Technology: Building Dna Gizmo Answer Key
DNA technology has revolutionized various fields, including medicine, forensics, and biotechnology. It enables us to manipulate and analyze DNA, providing insights into genetic disorders, identifying individuals, and developing novel treatments.
In medicine, DNA technology has paved the way for genetic testing, which allows for the early detection and diagnosis of inherited diseases such as cystic fibrosis and Huntington’s disease. It also aids in personalized medicine, tailoring treatments based on an individual’s genetic profile to improve outcomes.
Forensics
In forensics, DNA fingerprinting is a powerful tool for identifying individuals from crime scene evidence. By analyzing specific regions of DNA, forensic scientists can create unique profiles that can link suspects to crimes or exonerate the innocent.
Biotechnology
Biotechnology utilizes DNA technology to engineer organisms with desired traits. This has led to advancements in agriculture, such as creating genetically modified crops that are resistant to pests or have enhanced nutritional value. In the pharmaceutical industry, DNA technology enables the production of recombinant proteins, such as insulin, for therapeutic purposes.
Despite the immense benefits, DNA technology also raises ethical concerns. These include issues of privacy, discrimination based on genetic information, and the potential misuse of genetic data for nefarious purposes.
Question Bank
What is the purpose of the Building DNA Gizmo?
The Building DNA Gizmo is an interactive simulation that allows users to build and manipulate DNA molecules, providing a hands-on approach to understanding DNA structure and function.
How do I build a DNA molecule using the Gizmo?
To build a DNA molecule, select nucleotides from the library and connect them to form base pairs, following the rules of complementary base pairing.
What is the role of mutations in DNA?
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can have various effects, ranging from neutral to beneficial or harmful. They play a crucial role in genetic variation and evolution.