Prepare to embark on a captivating journey as we delve into the divisions of the New Testament. This comprehensive guide promises an immersive experience, unraveling the historical, literary, and theological significance of each section.
From the Gospels to Revelation, we’ll traverse the New Testament’s diverse landscape, examining its major divisions, their interconnections, and the profound impact they’ve had on Christian thought and practice.
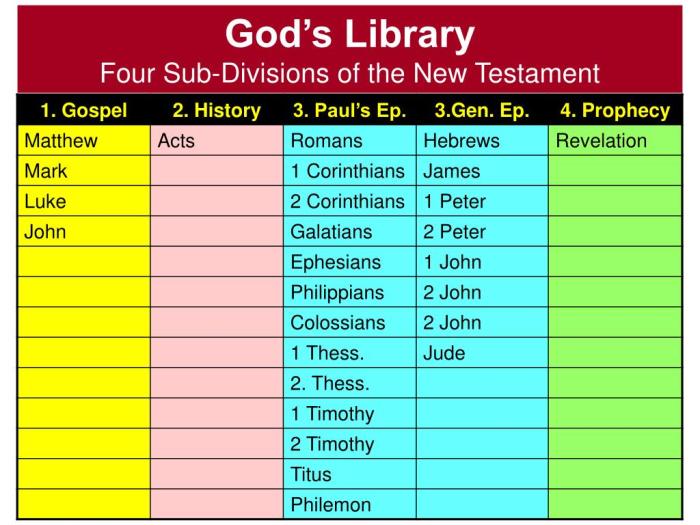
Gospels
The Gospels of Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John are the foundational texts of Christianity, providing diverse perspectives on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Each Gospel has its unique literary style, historical context, and theological emphasis, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of Jesus’ ministry and message.
Literary Styles
Matthew:Narrative and didactic, emphasizing Jesus’ teachings and their fulfillment of Old Testament prophecies. Mark:Fast-paced and action-packed, focusing on Jesus’ miracles and encounters with people. Luke:Orderly and comprehensive, presenting Jesus as a compassionate savior for all humanity. John:Poetic and symbolic, highlighting Jesus’ divine nature and relationship with God the Father.
Historical Contexts
Matthew:Written for a Jewish audience, emphasizing Jesus’ connection to the Old Testament and his role as the promised Messiah. Mark:Composed during the Roman persecution of Christians, emphasizing Jesus’ suffering and resurrection as a source of hope. Luke:Addressed to a Gentile audience, presenting Jesus as a universal savior who welcomes all people.
John:Written late in the first century, reflecting on Jesus’ life and teachings in light of early Christian controversies.
Theological Perspectives
Matthew:Jesus as the fulfillment of God’s covenant with Israel and the establishment of the Kingdom of God. Mark:Jesus as the suffering servant who brings salvation through his death and resurrection. Luke:Jesus as the compassionate savior who reveals God’s love and mercy to all.
John:Jesus as the divine Son of God who came to bridge the gap between humanity and God.
As we delve into the divisions of the New Testament, we encounter various legal principles that shape our understanding of the text. One such case that sheds light on the interpretation of religious texts is Parklane Hosiery Co. v. Shore . This landmark case highlights the importance of considering the historical and cultural context when interpreting religious scriptures, ultimately guiding us back to a deeper appreciation of the divisions of the New Testament.
Unique Contributions
Matthew:Provides extensive teachings on the Kingdom of God and Jesus’ ethical teachings (Sermon on the Mount). Mark:Emphasizes Jesus’ authority and power, as well as the disciples’ struggles and growth in faith. Luke:Includes unique parables and stories that highlight Jesus’ compassion and inclusiveness (Parable of the Good Samaritan).
John:Presents Jesus’ extended discourses on his relationship with God, the Holy Spirit, and eternal life.
Acts of the Apostles: Divisions Of The New Testament
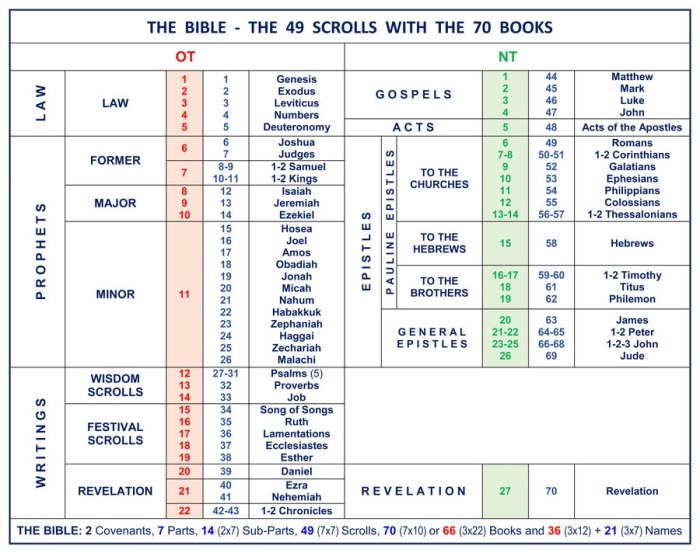
The Acts of the Apostles is a historical narrative that chronicles the growth and expansion of the early Christian Church. It serves as a bridge between the Gospels and the Epistles, providing a historical account of the events that shaped the development of Christianity.
The book of Acts highlights the pivotal role of the Holy Spirit in the spread of the Gospel. After Jesus’ ascension, the Holy Spirit descended upon the apostles, empowering them to proclaim the message of salvation to all nations.
The Role of the Holy Spirit
- Enabled the apostles to speak in different languages, overcoming linguistic barriers.
- Gave them boldness and courage to witness about Jesus, despite persecution.
- Guided them in their missionary journeys, leading them to specific individuals and places.
Historical and Theological Themes
The Acts of the Apostles explores several historical and theological themes:
- The Expansion of the Church:The book traces the spread of Christianity from Jerusalem to Rome, highlighting the establishment of new churches and the growth of the Christian community.
- The Conflict between Faith and Authority:The apostles faced opposition from Jewish and Roman authorities, who sought to suppress the spread of Christianity.
- The Importance of Community:The early Christian Church was characterized by a strong sense of community and fellowship, which played a vital role in its growth.
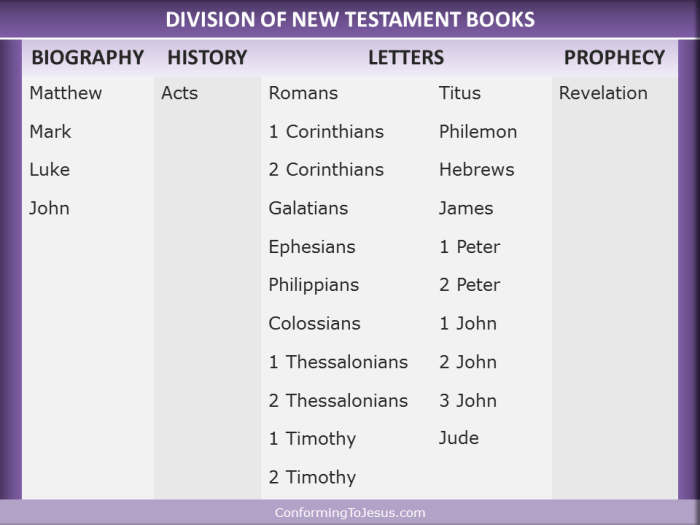
General Epistles
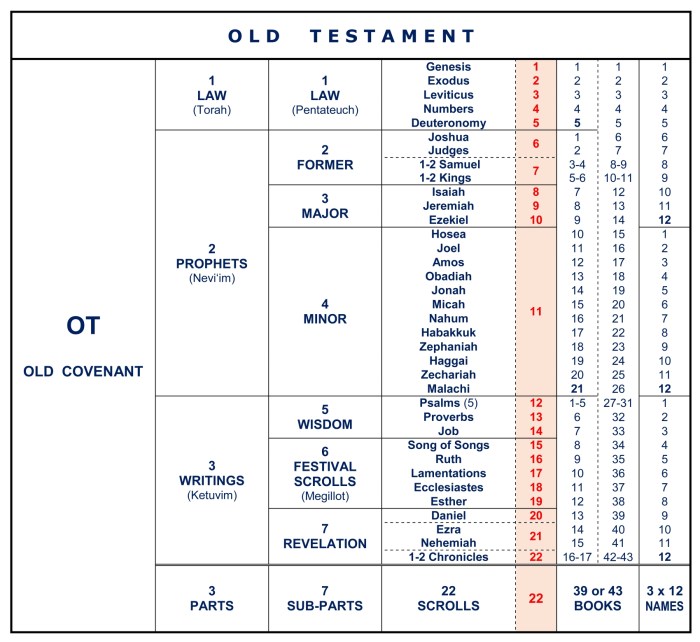
The General Epistles are a collection of seven letters in the New Testament that are not addressed to a specific individual or church but rather to a wider audience. These letters provide practical and theological guidance for Christian living and address a variety of topics, including faith, hope, love, and suffering.Authorship,
purpose, and key themes of each letter:
Hebrews, Divisions of the new testament
Authorship
Traditionally attributed to Paul, but modern scholarship questions this.
Purpose
To encourage Jewish Christians to remain faithful to Christ despite persecution.
Key themes
Jesus as the supreme high priest, the superiority of Christ’s priesthood to the Levitical priesthood, and the importance of faith and perseverance.
James
Authorship
James, the brother of Jesus.
Purpose
To provide practical guidance for Christian living, emphasizing the importance of faith and works.
Key themes
The relationship between faith and works, the dangers of wealth and pride, and the importance of wisdom and patience.
1 Peter
Authorship
Peter, the apostle.
Purpose
To encourage persecuted Christians to remain steadfast in their faith.
Key themes
The hope of salvation, the importance of suffering, and the need for unity and holiness.
2 Peter
Authorship
Traditionally attributed to Peter, but modern scholarship questions this.
Purpose
To warn against false teachers and encourage Christians to grow in faith and knowledge.
Key themes
The dangers of false teaching, the importance of Christian growth, and the certainty of Christ’s return.
1 John
Authorship
John, the apostle.
Purpose
To promote love, fellowship, and assurance of salvation among Christians.
Key themes
The love of God, the importance of obedience, and the assurance of eternal life.
2 John
Authorship
John, the apostle.
Purpose
To warn against false teachers and encourage Christians to remain faithful to the true faith.
Key themes
The dangers of false teaching, the importance of love, and the need for faithfulness.
3 John
Authorship
John, the apostle.
Purpose
To commend Gaius for his hospitality and encourage him to continue supporting the true faith.
Key themes
The importance of hospitality, the dangers of false teaching, and the need for faithfulness.
Jude
Authorship
Jude, the brother of James.
Purpose
To warn against false teachers and encourage Christians to contend for the true faith.
Key themes
The dangers of false teaching, the importance of faith, and the need for perseverance.
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of the divisions in the New Testament?
The divisions in the New Testament reflect the different purposes, perspectives, and historical contexts of the authors. They provide a structured framework for understanding the development of Christian thought and practice.
How do the Gospels differ from the Epistles?
The Gospels focus on the life and teachings of Jesus, while the Epistles are letters written by apostles and other early Christian leaders. The Epistles provide theological insights, pastoral guidance, and practical instructions for the early Church.
What is the Book of Revelation about?
The Book of Revelation is an apocalyptic text that presents visions of the end times and the ultimate victory of God. It contains symbolic language and imagery that has been interpreted in various ways throughout history.